Getting Started with Docker
NOTE: TT-Torch is deprecated. To work with PyTorch and the various features available in TT-Torch, please see the documentation for TT-XLA.
This document walks you through how to set up TT-Torch using a Docker image. There are two other available options for getting started:
- Installing a Wheel - if you do not want to use Docker, and prefer to use a virtual environment by itself instead, use this method.
- Building From Source - if you plan to develop TT-Torch further, you must build from source, and should use this method.
Configuring Hardware
Before setup can happen, you must configure your hardware. You can skip this section if you already completed the configuration steps. Otherwise, this section of the walkthrough shows you how to do a quick setup using TT-Installer.
-
Configure your hardware with TT-Installer using the Quick Installation section here.
-
Reboot your machine.
-
Make sure hugepages is enabled:
sudo systemctl enable --now 'dev-hugepages\x2d1G.mount'
sudo systemctl enable --now tenstorrent-hugepages.service
-
Please ensure that after you run the TT-Installer script, after you complete reboot and set up hugepages, you activate the virtual environment it sets up -
source ~/.tenstorrent-venv/bin/activate. -
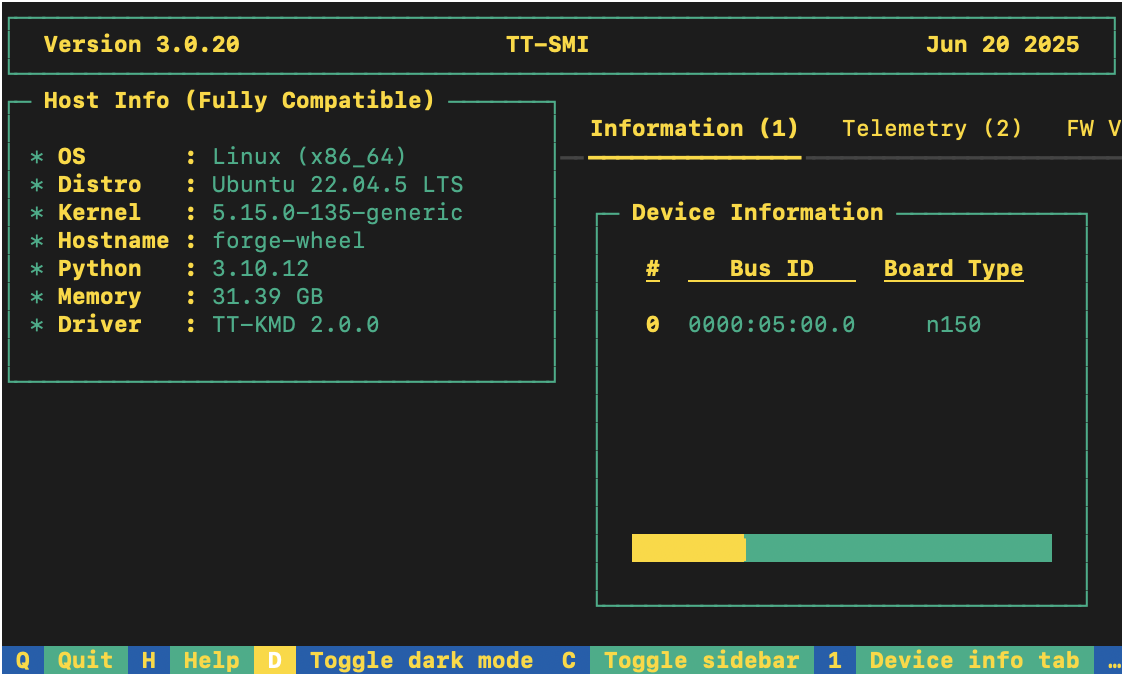
When your environment is running, to check that everything is configured, type the following:
tt-smi
You should see the Tenstorrent System Management Interface. It allows you to view real-time stats, diagnostics, and health info about your Tenstorrent device.
Setting up the Docker Container
This section walks through the installation steps for using a Docker container for your project.
To install, do the following:
- Install Docker if you do not already have it:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io -y
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
- Test that Docker is installed:
docker --version
- Add your user to the Docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
- Run the Docker container:
docker run -it --rm \
--device /dev/tenstorrent \
-v /dev/hugepages-1G:/dev/hugepages-1G \
ghcr.io/tenstorrent/tt-torch-slim:latest
NOTE: You cannot isolate devices in containers. You must pass through all devices even if you are only using one. You can do this by passing
--device /dev/tenstorrent. Do not try to pass--device /dev/tenstorrent/1or similar, as this type of device-in-container isolation will result in fatal errors later on during execution.
- If you want to check that it is running, open a new tab with the Same Command option and run the following:
docker ps
If all goes well, you are now ready to move on to the next section, and run your first demo model.
Running Models in Docker
This section shows you how to run a model using Docker. The provided example is from the TT-Forge repo. Do the following:
- Inside your running Docker container, clone the TT-Forge repo:
git clone https://github.com/tenstorrent/tt-forge.git
- Set the path for Python:
export PYTHONPATH=/tt-forge:$PYTHONPATH
- Navigate into TT-Forge and run the following command:
git submodule update --init --recursive
- For this set up, the resnet50_demo.py model is used. It requires additional dependencies be installed. Install the following:
pip install pillow
pip install tabulate
pip install requests
- Navigate into tt-forge/demos/tt-torch and run the model:
python resnet50_demo.py
If all goes well, you should get a list of top five predictions for what the example image is, with the top one being a cat.
Where to Go Next
Now that you have set up TT-Forge-FE, you can compile and run your own models, or continue trying demos from the TT-Torch folder in the TT-Forge repo.